AI-empowered Fluid Antenna Systems:Opportunities, Challenges, and Future Direction
Published in IEEE Wireless Communications, 2024
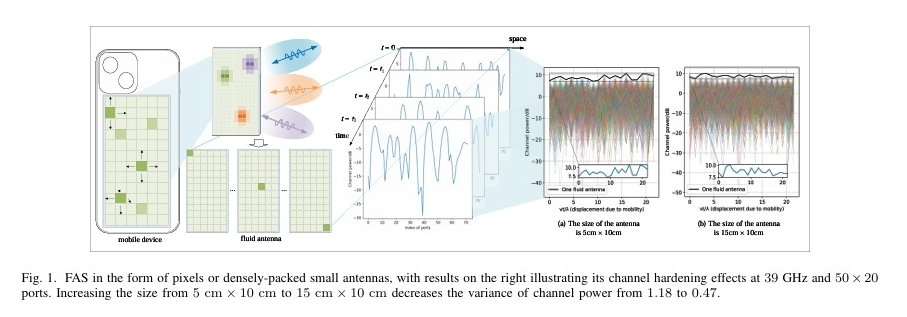 This article explores how AI empowers Fluid Antenna Systems (FAS) to enhance wireless communications by optimizing antenna positions and improving MIMO performance. It discusses opportunities, challenges, and future directions, using ISAC scenarios as a case study to illustrate potential gains.
This article explores how AI empowers Fluid Antenna Systems (FAS) to enhance wireless communications by optimizing antenna positions and improving MIMO performance. It discusses opportunities, challenges, and future directions, using ISAC scenarios as a case study to illustrate potential gains.
Recommended citation: Wang, Chao, et al. "AI-empowered fluid antenna systems: Opportunities, challenges, and future directions." IEEE Wireless Communications (2024).
Download Paper

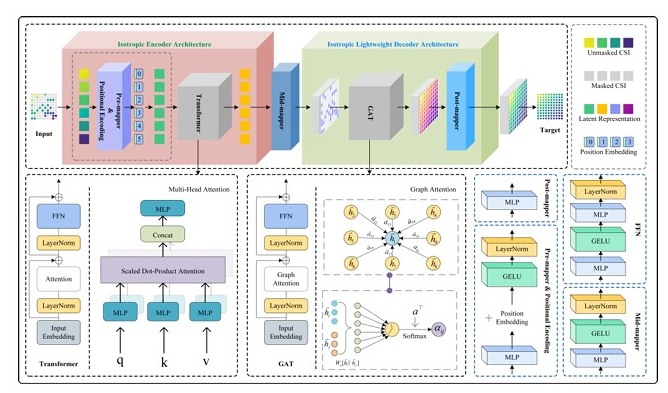 The paper proposes an asymmetric graph masked autoencoder (AGMAE) for channel state information (CSI) extrapolation in fluid antenna systems (FASs). The method leverages graph neural networks and attention mechanisms to reduce computational complexity and enhance generalization ability. Simulation results show that AGMAE achieves low prediction errors with only 5% observable antenna positions.
The paper proposes an asymmetric graph masked autoencoder (AGMAE) for channel state information (CSI) extrapolation in fluid antenna systems (FASs). The method leverages graph neural networks and attention mechanisms to reduce computational complexity and enhance generalization ability. Simulation results show that AGMAE achieves low prediction errors with only 5% observable antenna positions.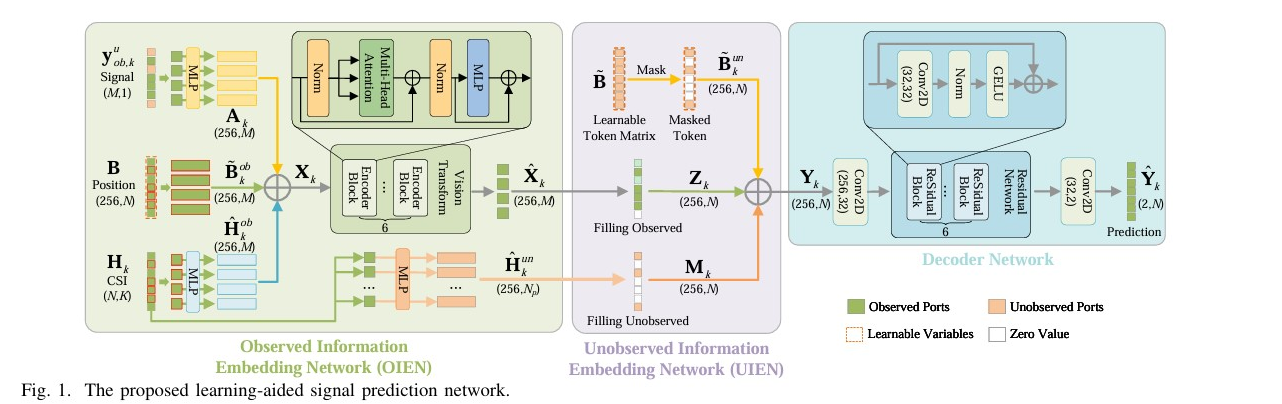 The article proposes a virtual Fluid Antenna System (FAS) using a transformer-based signal prediction network to infer received signals at imaginary antenna positions, enhancing MIMO receiver performance in multiuser channels.
The article proposes a virtual Fluid Antenna System (FAS) using a transformer-based signal prediction network to infer received signals at imaginary antenna positions, enhancing MIMO receiver performance in multiuser channels.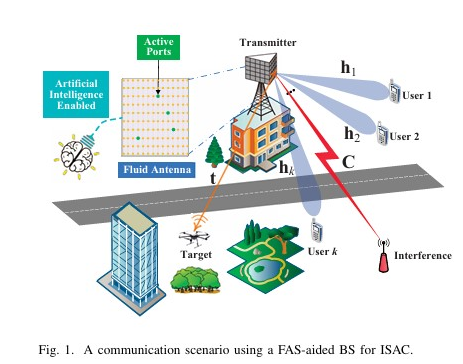 This paper investigates the joint optimization of port selection and precoding for a fluid antenna system (FAS)-assisted multiuser MIMO ISAC system using deep reinforcement learning to maximize the sum rate under a sensing constraint.
This paper investigates the joint optimization of port selection and precoding for a fluid antenna system (FAS)-assisted multiuser MIMO ISAC system using deep reinforcement learning to maximize the sum rate under a sensing constraint.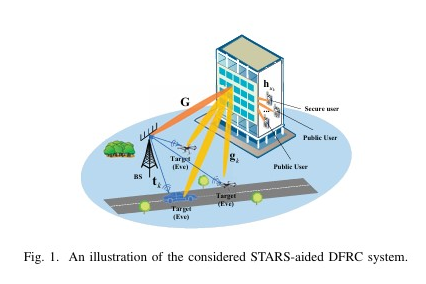 We proposes two novel iterative algorithms for interference alignment (IA) with symbol extensions in MIMO interference channels. The first algorithm minimizes the maximum per-user mean square error (MSE) while preserving the dimensionality of the desired signal. The second algorithm maximizes each receiver’s SINR while preserving the dimensionality of the desired signal.
We proposes two novel iterative algorithms for interference alignment (IA) with symbol extensions in MIMO interference channels. The first algorithm minimizes the maximum per-user mean square error (MSE) while preserving the dimensionality of the desired signal. The second algorithm maximizes each receiver’s SINR while preserving the dimensionality of the desired signal.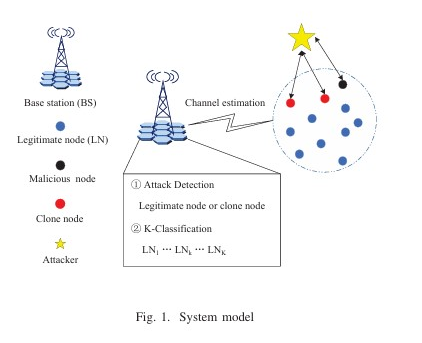 We proposes a deep learning-based PLA method for mmWave communications, using the spatiotemporal characteristics of mmWave channels as fingerprints to detect clone attacks and classify legitimate nodes via a novel complex-valued classifiable autoencoder and LSTM module, outperforming existing approaches.
We proposes a deep learning-based PLA method for mmWave communications, using the spatiotemporal characteristics of mmWave channels as fingerprints to detect clone attacks and classify legitimate nodes via a novel complex-valued classifiable autoencoder and LSTM module, outperforming existing approaches.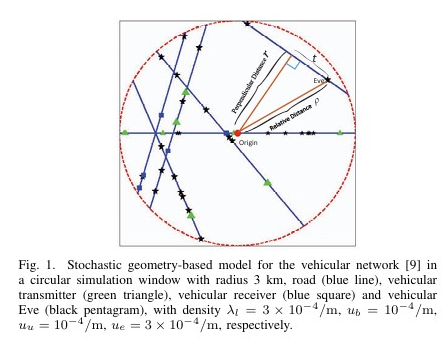 We proposes a symbol-level precoding-based scheme for STAR-RIS-aided dual-functional radar-communications (DFRC) systems. The aim is to securely transmit confidential information and perform target sensing concurrently. A joint optimization problem is formulated to maximize the average received radar sensing power, subject to constraints on communication users’ quality-of-service and security, as well as practical waveform design restrictions.
We proposes a symbol-level precoding-based scheme for STAR-RIS-aided dual-functional radar-communications (DFRC) systems. The aim is to securely transmit confidential information and perform target sensing concurrently. A joint optimization problem is formulated to maximize the average received radar sensing power, subject to constraints on communication users’ quality-of-service and security, as well as practical waveform design restrictions.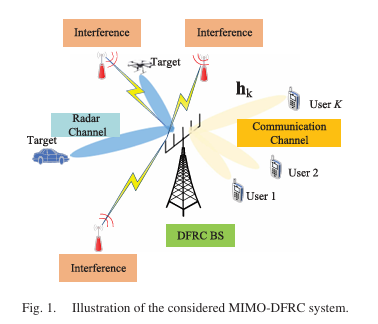 We proposes a symbol-level precoding-based scheme for STAR-RIS-aided dual-functional radar-communications (DFRC) systems. The aim is to securely transmit confidential information and perform target sensing concurrently. A joint optimization problem is formulated to maximize the average received radar sensing power, subject to constraints on communication users’ quality-of-service and security, as well as practical waveform design restrictions.
We proposes a symbol-level precoding-based scheme for STAR-RIS-aided dual-functional radar-communications (DFRC) systems. The aim is to securely transmit confidential information and perform target sensing concurrently. A joint optimization problem is formulated to maximize the average received radar sensing power, subject to constraints on communication users’ quality-of-service and security, as well as practical waveform design restrictions.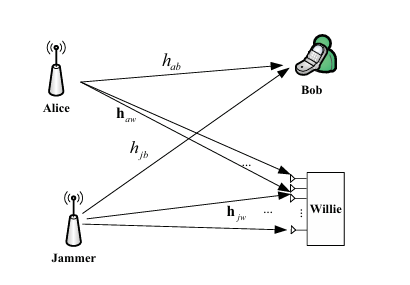 We investigates covert communication using a cooperative deception strategy against a multi-antenna adversary. It optimizes power allocation between a transmitter and a jammer under different CSI scenarios to maximize covert rate, showing improved performance and robustness compared to non-deception strategies.
We investigates covert communication using a cooperative deception strategy against a multi-antenna adversary. It optimizes power allocation between a transmitter and a jammer under different CSI scenarios to maximize covert rate, showing improved performance and robustness compared to non-deception strategies.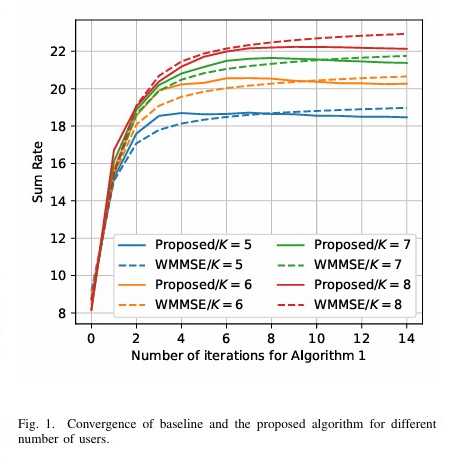 We proposes an ADMM-induced iterative algorithm to optimize the precoder for rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) in multi-antenna downlink systems. The algorithm transforms the non-convex problem into convex subproblems using WMMSE and solves them in closed form with ADMM, achieving faster convergence and lower complexity than existing methods.
We proposes an ADMM-induced iterative algorithm to optimize the precoder for rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) in multi-antenna downlink systems. The algorithm transforms the non-convex problem into convex subproblems using WMMSE and solves them in closed form with ADMM, achieving faster convergence and lower complexity than existing methods.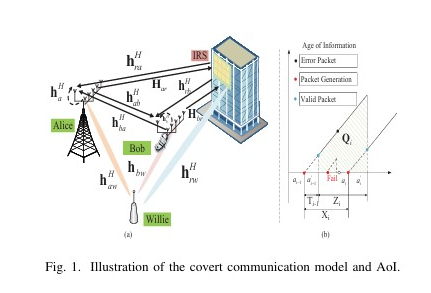 This paper investigates the minimization of covert information age in intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-aided covert communications, jointly optimizing active/passive beamforming and blocklength under covertness and AoI constraints.
This paper investigates the minimization of covert information age in intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-aided covert communications, jointly optimizing active/passive beamforming and blocklength under covertness and AoI constraints.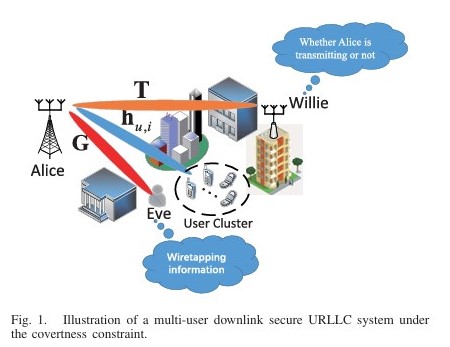 We proposes a symbol-level precoding-based scheme for STAR-RIS-aided dual-functional radar-communications (DFRC) systems. The aim is to securely transmit confidential information and perform target sensing concurrently. A joint optimization problem is formulated to maximize the average received radar sensing power, subject to constraints on communication users’ quality-of-service and security, as well as practical waveform design restrictions.
We proposes a symbol-level precoding-based scheme for STAR-RIS-aided dual-functional radar-communications (DFRC) systems. The aim is to securely transmit confidential information and perform target sensing concurrently. A joint optimization problem is formulated to maximize the average received radar sensing power, subject to constraints on communication users’ quality-of-service and security, as well as practical waveform design restrictions.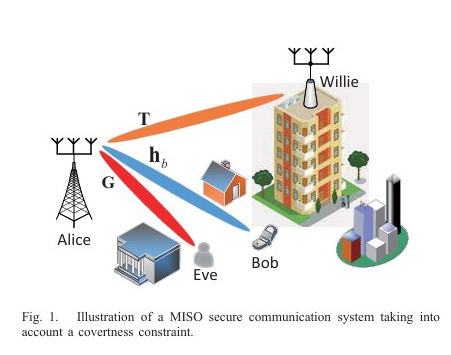 This paper proposes an optimal joint beamforming and jamming design for secure and covert ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) in a multiple-input single-output (MISO) downlink. The design aims to maximize the secrecy rate while satisfying covertness constraints, using a branch-reduce-and-bound (BRB) algorithm to solve the non-convex optimization problem.
This paper proposes an optimal joint beamforming and jamming design for secure and covert ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) in a multiple-input single-output (MISO) downlink. The design aims to maximize the secrecy rate while satisfying covertness constraints, using a branch-reduce-and-bound (BRB) algorithm to solve the non-convex optimization problem.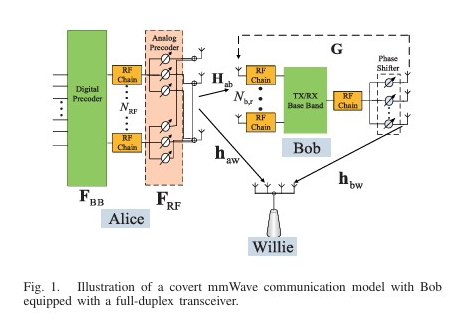 We investigates covert rate optimization for full-duplex millimeter wave communications. It proposes joint optimization frameworks for analog beamforming and jamming in both single and multiple data stream scenarios to maximize covert rate while satisfying detection error probability constraints, achieving significant performance gains.
We investigates covert rate optimization for full-duplex millimeter wave communications. It proposes joint optimization frameworks for analog beamforming and jamming in both single and multiple data stream scenarios to maximize covert rate while satisfying detection error probability constraints, achieving significant performance gains.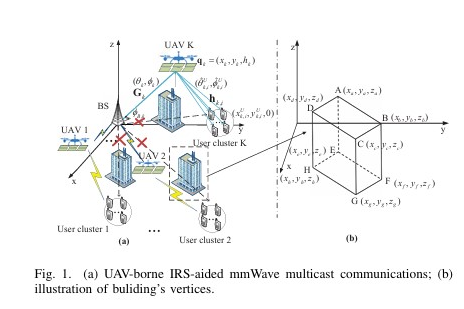 We design a resource allocation algorithm for UAV-borne IRS-aided mmWave multicast communications, jointly optimizing UAV placement, beamforming at the BS, and passive beamforming at the IRSs to maximize the minimum rate of user clusters.
We design a resource allocation algorithm for UAV-borne IRS-aided mmWave multicast communications, jointly optimizing UAV placement, beamforming at the BS, and passive beamforming at the IRSs to maximize the minimum rate of user clusters.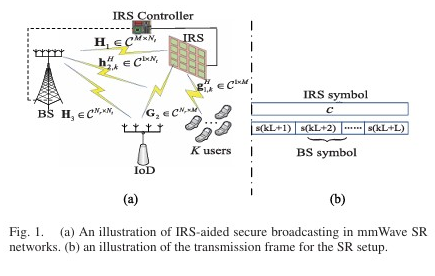 We investigates secure broadcast communications in IRS-aided mmWave symbiotic radio networks, where the IRS assists the BS in secure broadcasting while delivering its own information to an IoT device. The authors aim to maximize the minimum secrecy rate of multiple users by jointly designing the hybrid precoder at the BS and the passive beamformer at the IRS, subject to rate constraints. A computationally efficient iterative algorithm based on successive convex approximation is developed to solve the non-convex optimization problem. Simulation results validate the algorithm’s efficiency and superiority in improving the secrecy performance of the network.
We investigates secure broadcast communications in IRS-aided mmWave symbiotic radio networks, where the IRS assists the BS in secure broadcasting while delivering its own information to an IoT device. The authors aim to maximize the minimum secrecy rate of multiple users by jointly designing the hybrid precoder at the BS and the passive beamformer at the IRS, subject to rate constraints. A computationally efficient iterative algorithm based on successive convex approximation is developed to solve the non-convex optimization problem. Simulation results validate the algorithm’s efficiency and superiority in improving the secrecy performance of the network.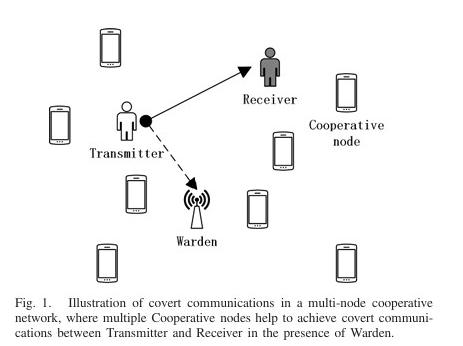 We investigates wireless covert communications aided by distributed cooperative jamming over slow fading channels. It proposes an uncoordinated jammer selection scheme where friendly nodes with low channel gains to the receiver are chosen as jammers to confuse the warden. The optimal selection threshold and transmission rate are jointly designed to maximize covert throughput under a covertness constraint. Results show that the multi-jammer scheme outperforms single-jammer methods and that the covert throughput improves significantly with more cooperative nodes, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed scheme.
We investigates wireless covert communications aided by distributed cooperative jamming over slow fading channels. It proposes an uncoordinated jammer selection scheme where friendly nodes with low channel gains to the receiver are chosen as jammers to confuse the warden. The optimal selection threshold and transmission rate are jointly designed to maximize covert throughput under a covertness constraint. Results show that the multi-jammer scheme outperforms single-jammer methods and that the covert throughput improves significantly with more cooperative nodes, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed scheme.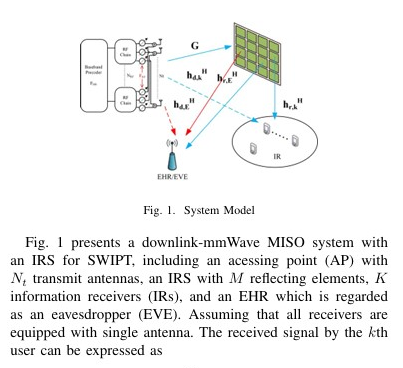 This paper investigates the hybrid precoding design for an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted mmWave communication system with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT). The authors propose a joint optimization of the hybrid precoders and the phase shifts of the IRS to maximize the secrecy rate while satisfying energy harvesting and power constraints.
This paper investigates the hybrid precoding design for an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted mmWave communication system with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT). The authors propose a joint optimization of the hybrid precoders and the phase shifts of the IRS to maximize the secrecy rate while satisfying energy harvesting and power constraints.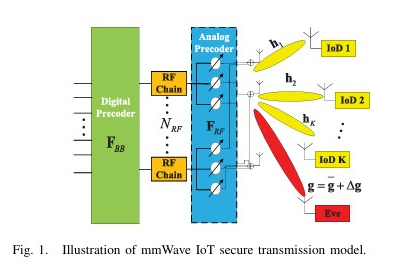 The paper proposes a robust hybrid precoding scheme for securing mmWave IoT networks under secrecy outage constraints. It maximizes the minimum secrecy rate among IoT devices by jointly optimizing analog and digital precoders using the PDD method, achieving significant performance gains.
The paper proposes a robust hybrid precoding scheme for securing mmWave IoT networks under secrecy outage constraints. It maximizes the minimum secrecy rate among IoT devices by jointly optimizing analog and digital precoders using the PDD method, achieving significant performance gains.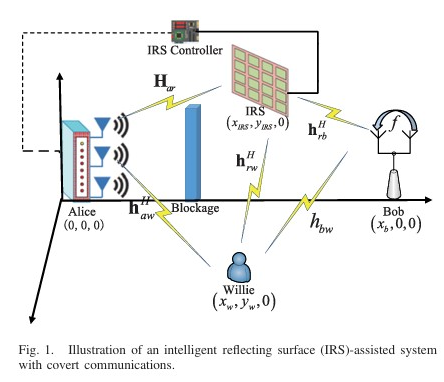 We investigates the joint active and passive beamforming optimization for intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted multi-antenna covert communications to maximize the covert rate while satisfying detection error probability and outage constraints.
We investigates the joint active and passive beamforming optimization for intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted multi-antenna covert communications to maximize the covert rate while satisfying detection error probability and outage constraints.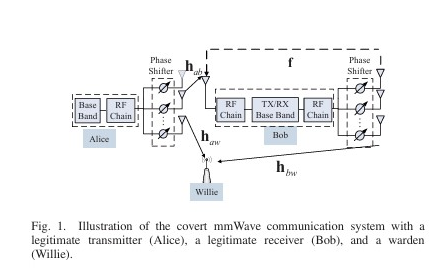 This paper investigates covert millimeter-wave (mmWave) communications, where a multi-antenna transmitter (Alice) sends information covertly to a full-duplex receiver (Bob) in the presence of a warden (Willie). The authors jointly optimize the analog beamforming at Alice and Bob to maximize the covert rate while satisfying covertness and communication outage constraints.
This paper investigates covert millimeter-wave (mmWave) communications, where a multi-antenna transmitter (Alice) sends information covertly to a full-duplex receiver (Bob) in the presence of a warden (Willie). The authors jointly optimize the analog beamforming at Alice and Bob to maximize the covert rate while satisfying covertness and communication outage constraints.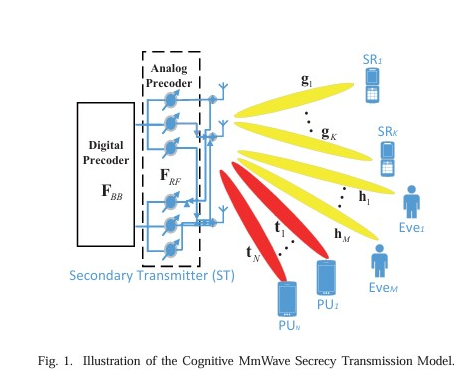 We investigates the hybrid secure precoder design for cognitive millimeter wave (mmWave) networks to enhance physical layer security. The authors aim to maximize the minimum secrecy rate of secondary users under constraints on interference power and quality of service. They formulate a non-convex optimization problem and propose a penalty dual decomposition (PDD) based iterative algorithm to solve it. Simulation results demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed algorithm in improving secrecy performance compared to traditional methods.
We investigates the hybrid secure precoder design for cognitive millimeter wave (mmWave) networks to enhance physical layer security. The authors aim to maximize the minimum secrecy rate of secondary users under constraints on interference power and quality of service. They formulate a non-convex optimization problem and propose a penalty dual decomposition (PDD) based iterative algorithm to solve it. Simulation results demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed algorithm in improving secrecy performance compared to traditional methods.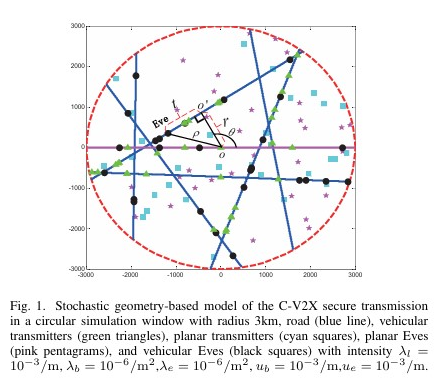 We investigates the physical layer security (PLS) of cellular vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X) networks using artificial noise (AN) and secure beamforming techniques. The authors build an analytical framework based on stochastic geometry to study the PLS of multi-antenna C-V2X networks. They derive closed-form expressions for coverage probability and secrecy probability and analyze the effective secrecy throughput to evaluate the network’s security performance. Simulation results show that increasing the number of transmit antennas improves the robustness of the secure transmission strategy and that the optimal power allocation ratio between confidential information and AN remains relatively stable for different numbers of antennas.
We investigates the physical layer security (PLS) of cellular vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X) networks using artificial noise (AN) and secure beamforming techniques. The authors build an analytical framework based on stochastic geometry to study the PLS of multi-antenna C-V2X networks. They derive closed-form expressions for coverage probability and secrecy probability and analyze the effective secrecy throughput to evaluate the network’s security performance. Simulation results show that increasing the number of transmit antennas improves the robustness of the secure transmission strategy and that the optimal power allocation ratio between confidential information and AN remains relatively stable for different numbers of antennas.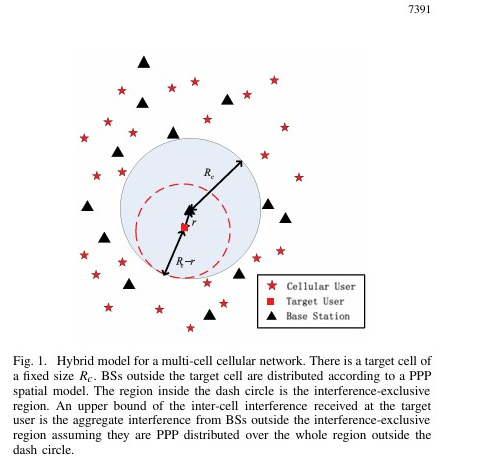 The paper investigates the impact of artificial noise (AN) on cellular network security using stochastic geometry. It analyzes connection and secrecy outages in a target cell, considering pilot contamination and inter-cell interference. Results show AN can enhance security but also increase interference, requiring optimized power allocation.
The paper investigates the impact of artificial noise (AN) on cellular network security using stochastic geometry. It analyzes connection and secrecy outages in a target cell, considering pilot contamination and inter-cell interference. Results show AN can enhance security but also increase interference, requiring optimized power allocation.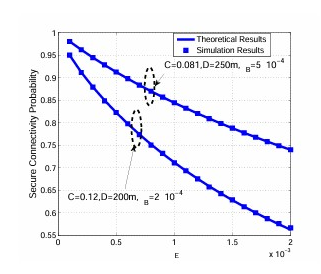 This paper investigates the physical layer security of millimeter wave (mmWave) cellular networks using stochastic geometry. It analyzes the secure connectivity probability and average number of perfect communication links per unit area for both noise-limited and interference-limited scenarios, considering non-colluding and colluding eavesdroppers. The study shows the importance of antenna array patterns and eavesdropper intensity in determining the secrecy performance and provides insights into optimal power allocation for artificial noise in mmWave networks.
This paper investigates the physical layer security of millimeter wave (mmWave) cellular networks using stochastic geometry. It analyzes the secure connectivity probability and average number of perfect communication links per unit area for both noise-limited and interference-limited scenarios, considering non-colluding and colluding eavesdroppers. The study shows the importance of antenna array patterns and eavesdropper intensity in determining the secrecy performance and provides insights into optimal power allocation for artificial noise in mmWave networks.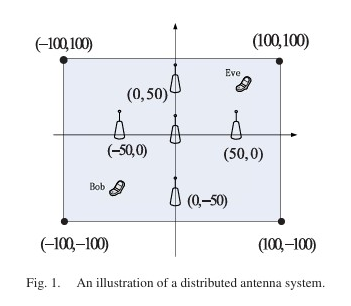 The paper proposes a distributed artificial noise scheme for enhancing security in distributed antenna systems (DAS) by optimizing power allocation to maximize the ergodic secrecy rate (ESR) using large-scale CSI.
The paper proposes a distributed artificial noise scheme for enhancing security in distributed antenna systems (DAS) by optimizing power allocation to maximize the ergodic secrecy rate (ESR) using large-scale CSI.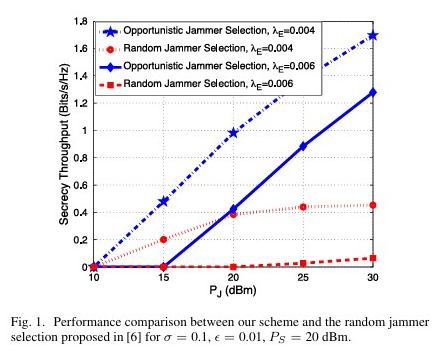 We proposes an opportunistic jammer selection scheme for enhancing security in a single-input–single-output multieavesdropper (SISOME) channel using stochastic geometry modeling and analysis. The scheme selects jammers based on their channel gains to the legitimate receiver, allowing them to transmit independent Gaussian jamming signals to confuse eavesdroppers. The authors derive the secrecy throughput and prove it is a quasi-concave function of the selection threshold, enabling efficient optimization. Simulation results demonstrate significant improvements in secrecy performance compared to random jammer selection schemes.
We proposes an opportunistic jammer selection scheme for enhancing security in a single-input–single-output multieavesdropper (SISOME) channel using stochastic geometry modeling and analysis. The scheme selects jammers based on their channel gains to the legitimate receiver, allowing them to transmit independent Gaussian jamming signals to confuse eavesdroppers. The authors derive the secrecy throughput and prove it is a quasi-concave function of the selection threshold, enabling efficient optimization. Simulation results demonstrate significant improvements in secrecy performance compared to random jammer selection schemes.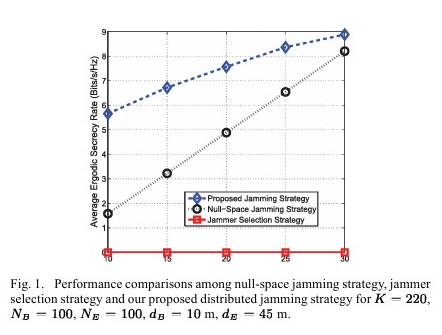 The paper proposes a low-overhead distributed jamming strategy to enhance SIMO secrecy transmission, optimizing jamming power based on statistical CSI for better physical layer security in massive MIMO systems.
The paper proposes a low-overhead distributed jamming strategy to enhance SIMO secrecy transmission, optimizing jamming power based on statistical CSI for better physical layer security in massive MIMO systems.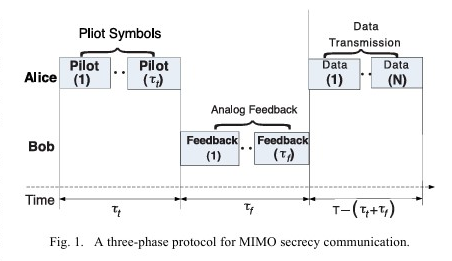 This paper proposes a framework for artificial noise-assisted secure transmission in MIMOME channels under training and feedback, optimizing power allocation and training overhead to maximize effective ergodic secrecy rate.
This paper proposes a framework for artificial noise-assisted secure transmission in MIMOME channels under training and feedback, optimizing power allocation and training overhead to maximize effective ergodic secrecy rate.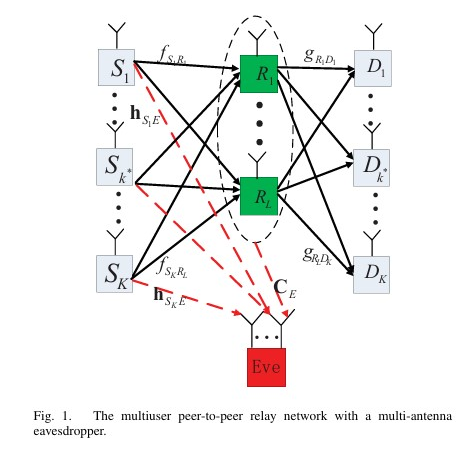 We proposes a joint beamforming and power allocation strategy for maximizing secrecy rate in multiuser peer-to-peer relay networks with a multi-antenna eavesdropper. By using null space beamforming to eliminate information leakage and sequential parametric convex approximation to solve the non-convex problem, the proposed method achieves significant performance improvements in secrecy rate, as demonstrated by simulations.
We proposes a joint beamforming and power allocation strategy for maximizing secrecy rate in multiuser peer-to-peer relay networks with a multi-antenna eavesdropper. By using null space beamforming to eliminate information leakage and sequential parametric convex approximation to solve the non-convex problem, the proposed method achieves significant performance improvements in secrecy rate, as demonstrated by simulations.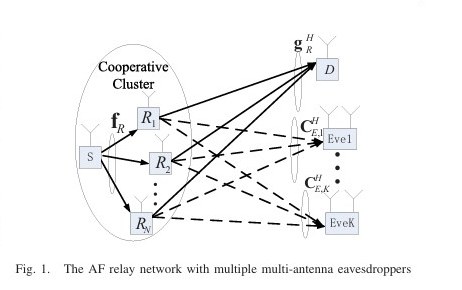 This paper proposes a robust joint design of distributed beamforming and artificial noise for secure amplify-and-forward (AF) relay networks in the presence of multiple multi-antenna eavesdroppers. The authors aim to maximize the worst-case secrecy rate under the total power constraint of all relay nodes, using semidefinite relaxation (SDR) and a one-dimensional search involving semidefinite programming (SDP).
This paper proposes a robust joint design of distributed beamforming and artificial noise for secure amplify-and-forward (AF) relay networks in the presence of multiple multi-antenna eavesdroppers. The authors aim to maximize the worst-case secrecy rate under the total power constraint of all relay nodes, using semidefinite relaxation (SDR) and a one-dimensional search involving semidefinite programming (SDP).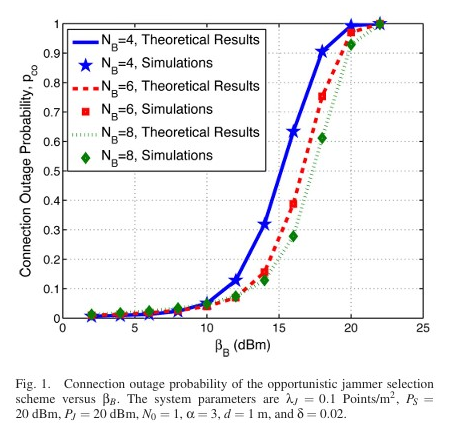 The paper proposes an opportunistic jammer selection scheme for the SIMOME wiretap channel. It selects single-antenna jammers to transmit Gaussian jamming signals to confuse eavesdroppers without centralized coordination. The scheme optimizes the selection threshold to maximize secrecy throughput and ergodic secrecy rate, achieving significant performance gains over random jammer selection.
The paper proposes an opportunistic jammer selection scheme for the SIMOME wiretap channel. It selects single-antenna jammers to transmit Gaussian jamming signals to confuse eavesdroppers without centralized coordination. The scheme optimizes the selection threshold to maximize secrecy throughput and ergodic secrecy rate, achieving significant performance gains over random jammer selection.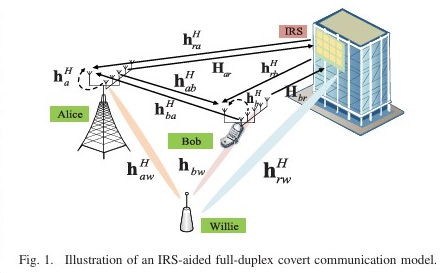 The paper proposes two strategies to maximize the secrecy throughput of the primary user in a cognitive radio network by optimizing beamforming, rate parameters, and power allocation between the information signal and artificial noise of the secondary user, subject to secrecy outage and throughput constraints.
The paper proposes two strategies to maximize the secrecy throughput of the primary user in a cognitive radio network by optimizing beamforming, rate parameters, and power allocation between the information signal and artificial noise of the secondary user, subject to secrecy outage and throughput constraints.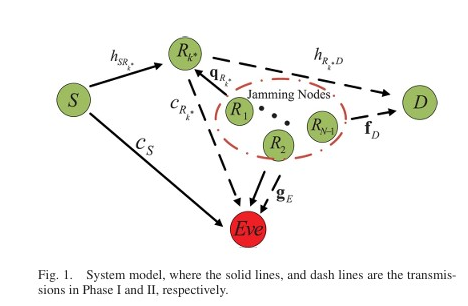 We proposes a hybrid opportunistic relaying and jamming scheme with power allocation to enhance security in cooperative networks. The study optimizes power allocation to maximize the ergodic secrecy rate (ESR) and analyzes the impact of outdated CSI and multiple eavesdroppers on the proposed scheme.
We proposes a hybrid opportunistic relaying and jamming scheme with power allocation to enhance security in cooperative networks. The study optimizes power allocation to maximize the ergodic secrecy rate (ESR) and analyzes the impact of outdated CSI and multiple eavesdroppers on the proposed scheme.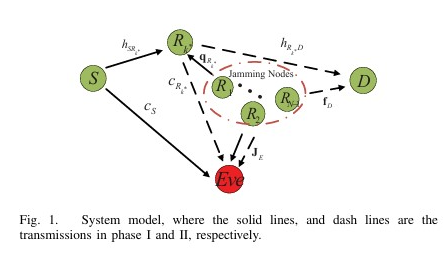 This paper proposes a joint relay selection and artificial jamming power allocation scheme for secure decode-and-forward (DF) relay networks. The authors aim to maximize the ergodic secrecy rate (ESR) by optimizing the power allocation between the confidential information and jamming signals, using only statistical channel state information (CSI) of the eavesdropper.
This paper proposes a joint relay selection and artificial jamming power allocation scheme for secure decode-and-forward (DF) relay networks. The authors aim to maximize the ergodic secrecy rate (ESR) by optimizing the power allocation between the confidential information and jamming signals, using only statistical channel state information (CSI) of the eavesdropper.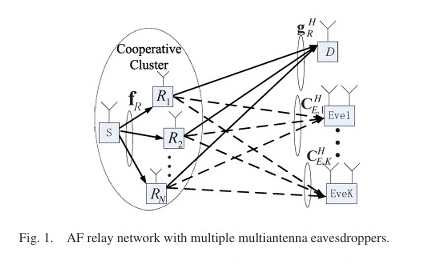 The paper proposes a robust joint CB and CJ design for an AF relay network with multiple eavesdroppers and imperfect CSI. Using SDR and ICA, the nonconvex problem is transformed into a sequence of convex problems to maximize the worst-case secrecy rate. The proposed design is efficient and guarantees convergence to a KKT solution.
The paper proposes a robust joint CB and CJ design for an AF relay network with multiple eavesdroppers and imperfect CSI. Using SDR and ICA, the nonconvex problem is transformed into a sequence of convex problems to maximize the worst-case secrecy rate. The proposed design is efficient and guarantees convergence to a KKT solution.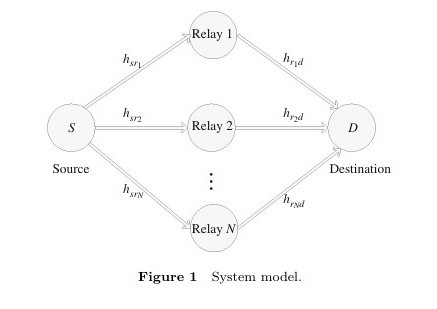 This research proposes a novel relay selection strategy for amplify-and-forward cooperative networks with outdated channel state information (CSI). By combining outdated and statistical CSI, the strategy optimizes symbol error probability (SEP) and outage probability at high SNR, achieving better performance than traditional methods in asymmetrical networks.
This research proposes a novel relay selection strategy for amplify-and-forward cooperative networks with outdated channel state information (CSI). By combining outdated and statistical CSI, the strategy optimizes symbol error probability (SEP) and outage probability at high SNR, achieving better performance than traditional methods in asymmetrical networks. This paper proposes a novel one-sided algorithm for interference alignment (IA) in constant MIMO interference channels, using the steepest descent method to design linear precoders at transmitters only. The algorithm aims to minimize the spatial distance between different interference subspaces to achieve IA, avoiding the need for alternating between transmitters and receivers.
This paper proposes a novel one-sided algorithm for interference alignment (IA) in constant MIMO interference channels, using the steepest descent method to design linear precoders at transmitters only. The algorithm aims to minimize the spatial distance between different interference subspaces to achieve IA, avoiding the need for alternating between transmitters and receivers.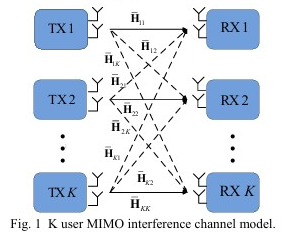 This paper proposes two novel iterative algorithms for interference alignment (IA) with symbol extensions in MIMO interference channels. The first algorithm minimizes the maximum per-user mean square error (MSE) while preserving the dimensionality of the desired signal. The second algorithm maximizes each receiver’s SINR while preserving the dimensionality of the desired signal.
This paper proposes two novel iterative algorithms for interference alignment (IA) with symbol extensions in MIMO interference channels. The first algorithm minimizes the maximum per-user mean square error (MSE) while preserving the dimensionality of the desired signal. The second algorithm maximizes each receiver’s SINR while preserving the dimensionality of the desired signal.